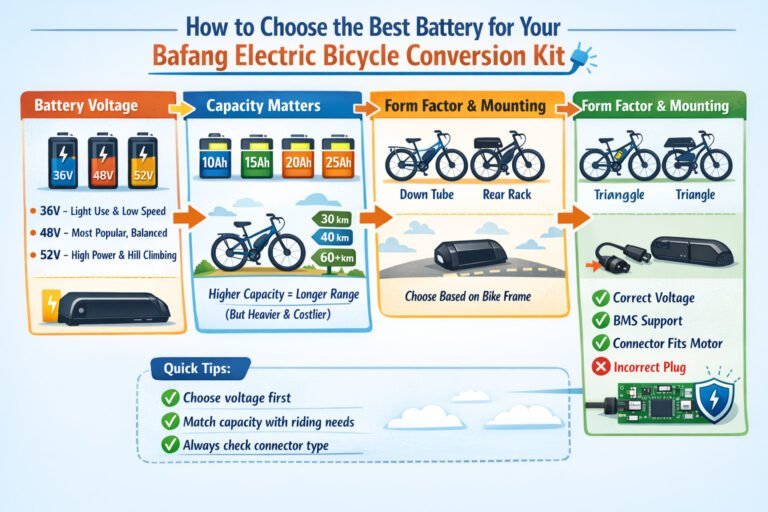
In today’s fast-growing electric mobility and renewable energy sectors, lithium battery technology continues to advance rapidly. However, high energy density and complex electrochemistry bring both performance and safety challenges. That’s where the Battery Management System (BMS) comes in. When we refer to a BMS battery, we’re talking about a battery pack equipped with an intelligent system designed to monitor, protect, and optimize its performance.
In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into what a BMS battery is, how it works, the key functions of a BMS, its types, and why BMS-equipped batteries are critical in modern applications such as eBikes, electric , solar energy storage systems, and industrial automation.
What Is a BMS Battery?
A BMS battery refers to a lithium battery pack that integrates a Battery Management System—an intelligent electronic system that supervises battery operation to ensure safety, performance, and longevity.
In essence, a BMS acts as the brain of the battery. It continually collects and processes data such as:
Voltage of each cell
Temperature
State of Charge (SOC)
Current flow
Cell balancing status
Fault detection
Based on this data, the BMS controls charge/discharge cycles, communicates with external systems (such as vehicle controllers or inverters), and triggers protective measures when abnormal conditions occur.
Why Is BMS Important for Lithium Batteries?
Unlike traditional lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries are more sensitive to:
Overcharging – which can lead to overheating, swelling, or even fire
Over-discharging – which can permanently damage the battery
Thermal runaway – where high temperatures trigger internal short circuits
Cell imbalance – causing uneven wear and reduced battery life
A BMS ensures that each individual cell within the pack operates within safe parameters. Without a BMS, lithium batteries could become unreliable or dangerous, especially in high-drain or high-temperature applications.
Key Functions of a Battery Management System
Voltage Monitoring
The BMS tracks the voltage of each individual cell and the overall pack voltage. If any cell exceeds the safe voltage threshold during charging or drops too low during discharging, the BMS will cut off the process to prevent damage.
Temperature Monitoring
Thermal sensors measure the battery’s internal and external temperature. If the temperature exceeds limits, the BMS can slow charging or shut the battery down to avoid overheating.
Current Monitoring and Short Circuit Protection
By constantly tracking current, the BMS protects against:
- Overcurrent conditions
- Short circuits
- Reverse polarity
This is critical in high-load applications like electric bikes or power tools.
State of Charge (SOC) Estimation
The BMS calculates the remaining charge of the battery (like a fuel gauge for your battery). It does this using algorithms like Coulomb counting and voltage-based estimation.
State of Health (SOH) Analysis
The BMS tracks degradation over time, offering users insight into the battery’s life expectancy and performance level.
Cell Balancing
Lithium cells can become unbalanced over time. The BMS actively redistributes energy between cells to ensure uniform voltage, improving longevity and capacity.
Communication Interface
Modern BMS systems feature CAN bus, UART, RS485, SMBus, or I²C protocols to communicate with external systems like:
- Electric bike controllers
- Solar inverters
- Energy management systems (EMS)
- Vehicle ECUs
Types of BMS Systems
BMS systems come in several architectures:
- Centralized BMS
All functions and sensors are housed on a single control board. This is common in small to medium battery packs like eBikes or UPS systems.
- Distributed BMS
Each cell or module has its own small monitoring unit. These units send data to a master controller. Suitable for large-scale systems like EVs or solar arrays.
- Modular BMS
A hybrid approach that combines centralized control with modular cell management. It provides flexibility for medium to large applications.
Applications of BMS Batteries
✅ Electric Bicycles (eBikes)
A reliable BMS ensures safe charging, consistent power output, and real-time communication with the eBike controller. Modern BMS systems also support Bluetooth for app-based diagnostics.
✅ Electric Mobility
In electric mobility, the BMS handles thousands of individual cells, ensuring consistent performance, safety, and integration with regenerative braking and powertrain systems.
✅ Energy Storage Systems (ESS)
For solar and wind storage, the BMS manages large-scale lithium battery banks, maintaining stability under fluctuating loads and renewable inputs.
✅ Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS)
A BMS-equipped battery protects mission-critical equipment by ensuring smooth and safe power backup operations.
✅ Robotics and AGVs
Industrial robots and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) rely on high-performance lithium packs with robust BMS control for precision, safety, and long lifecycle.
What Makes a High-Quality BMS Battery?
Not all BMS batteries are created equal. Key features of a reliable BMS battery include:
- Accurate SOC/SOH estimation
- High-speed communication protocols (CAN/UART)
- Robust thermal and current protection
- Intelligent fault detection and logging
- Waterproof or ruggedized housing (IP65/IP67 rated)
- Certification compliance (UN38.3, CE, EN 50604, etc.)
BMS Battery Trends in 2025
The battery industry is evolving. Some emerging BMS battery trends include:
AI-powered BMS for predictive diagnostics
Cloud-connected BMS for remote monitoring and fleet management
Smart BMS with Bluetooth or mobile app connectivity
Automotive-grade safety standards (ISO 26262)
Integration with fast charging systems (CCS, GB/T)
A BMS battery is more than just a lithium pack—it’s a smart, self-protecting, high-performance energy solution. Whether you’re powering an electric bike, running a solar energy system, or building autonomous robots, integrating a reliable Battery Management System is essential to maximize efficiency, safety, and lifecycle.
As lithium battery technology continues to evolve, the role of the BMS becomes even more critical. Choosing a battery with a robust and intelligent BMS is not just a matter of performance—it’s a matter of trust.